Imagine transforming your backyard into a flourishing oasis, teeming with an abundance of fresh vegetables and vibrant flowers. If you’ve ever wondered how to maximize productivity in your garden, look no further. In this article, we will explore effective strategies and techniques to plan a garden layout that not only beautifies your space but also yields bountiful harvests. From considering sunlight exposure to companion planting, get ready to unlock the secrets to a thriving garden that will have you reaping the rewards all season long.
Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing the Right Location
Understanding Light Conditions
When choosing a location for your garden, one of the most important factors to consider is the availability of sunlight. Most plants need a minimum of 6 hours of direct sunlight each day to thrive. Before selecting a spot, take note of how the sun moves across your yard throughout the day. Observe any areas that receive full sun, partial shade, or full shade. By understanding the light conditions in different areas of your yard, you can strategically place your plants accordingly, ensuring they have the optimal amount of sunlight.
Assessing Soil Quality
Another crucial aspect to consider when choosing a garden location is the quality of the soil. Different plants have different soil requirements, so it’s essential to assess the soil’s characteristics before planting. Conduct a soil test to determine its pH level and nutrient content. This will help you identify any deficiencies or imbalances that need to be addressed. Additionally, consider the soil’s texture and drainage capabilities. Sandy soil drains quickly but may require more frequent watering, while clay soil retains water but can become compacted. By understanding the soil quality, you can make informed decisions about which plants will thrive in your garden.
Considering Microclimates
Microclimates are small, localized areas within your garden that have unique climate conditions. They can be created by factors such as buildings, trees, or slopes. By identifying microclimates in your garden, you can effectively utilize these variations to your advantage. For example, areas near walls or buildings may absorb and radiate heat, creating a warmer microclimate suitable for heat-loving plants. In contrast, shaded areas or those near water bodies may provide cooler conditions, ideal for shade-loving plants. By considering microclimates, you can maximize the productivity of your garden by growing plants in the areas that best suit their specific climate needs.
Analyzing Planting Zones
Determining Your Hardiness Zone
Plant hardiness zones provide valuable information about the climatic conditions in a particular area and help gardeners make informed decisions about which plants are likely to thrive. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has divided the country into different hardiness zones based on average annual minimum temperatures. By determining your hardiness zone, you can select plants that are well-suited to your specific climate and ensure their success. Several online resources and gardening books provide zone maps that make it easy to identify your zone.
Exploring Climate Considerations
Beyond hardiness zones, it is essential to consider other climate factors that can impact your garden’s productivity. For example, the average annual rainfall, humidity levels, and frost dates in your region can all play a significant role in determining which plants will flourish. By understanding your local climate, you can choose plants that are resilient and adapted to your area’s specific conditions. Additionally, familiarize yourself with any microclimates within your garden, as these can create unique climate conditions that may require special considerations when selecting plants.
Working with Available Space
Plot Size and Shape
The size and shape of your garden plot will directly impact the layout and arrangement of your plants. Consider the available space and how much area you are willing to dedicate to your garden. A larger plot will allow for greater plant diversity and the opportunity to experiment with different planting techniques. However, even a small plot can be productive if planned effectively. Additionally, consider the shape of your plot. Rectangular or square plots are more straightforward to work with and allow for neat rows or organized sections. Irregularly shaped plots may require more creativity and strategic planning.
Vertical Gardening
If you have limited horizontal space in your garden, vertical gardening is an excellent solution for maximizing your productivity. Vertical gardening utilizes vertical wall space, trellises, or structures to grow plants vertically instead of horizontally. This technique is particularly useful for vining plants such as cucumbers, beans, and tomatoes. By training the plants to grow vertically, you can save valuable ground space and increase your overall planting capacity. Additionally, vertical gardening can create an aesthetically pleasing and visually interesting garden design.
Utilizing Containers and Raised Beds
Containers and raised beds are great options for gardeners with limited space or poor soil quality. Containers, such as pots or planters, are versatile and can be placed on patios, balconies, or even windowsills. Raised beds, on the other hand, are elevated planting areas built on top of the existing soil. Both options provide better control over soil quality, drainage, and weed management. They also allow for easier access and maintenance, reducing the strain on your back and knees. Container gardens and raised beds can be organized based on plant variety or specific themes, adding beauty and functionality to your garden.
Companion Planting
Companion planting refers to the strategic placement of plants that have beneficial relationships with one another. By companion planting, you can maximize space utilization and create symbiotic relationships between plants. For example, planting tall sun-loving crops, such as corn, can provide shade for lower-growing plants, like lettuce or spinach. Additionally, certain combinations of plants can help repel pests, attract beneficial insects, or enhance the flavor and growth of neighboring plants. Understanding companion planting principles can help you make the most of your available space and foster a healthy and diverse garden ecosystem.
Creating Functional Zones
Dividing the Garden into Zones
Dividing your garden into functional zones allows for better organization, improved efficiency, and easier maintenance. Start by assessing your gardening needs and priorities. Consider separating areas for growing different types of plants, such as vegetables, herbs, or flowers. You can also create zones based on the frequency of maintenance tasks, grouping plants that require similar care together. Additionally, think about creating designated areas for relaxation or entertainment to make the most of your garden space. By organizing your garden into zones, you can streamline your gardening tasks and create a visually appealing and functional outdoor space.
Organizing by Planting Frequency
Plants have different growth rates and harvesting times, which means they require varying planting and maintenance schedules. By organizing your garden based on planting frequency, you can effectively utilize your available space and ensure a continuous supply of fresh produce. Consider grouping fast-growing plants together in one area, allowing for quick succession planting and harvesting. Planting slower-growing or long-lasting crops in another area will ensure a more extended harvest period. By considering planting frequency when designing your garden layout, you can maximize its productivity throughout the growing season.
Designating Specialty Areas
Designating specialty areas within your garden can add both functionality and beauty to your overall layout. Create a separate area for herbs, where you can easily access fresh ingredients for cooking or medicinal purposes. Consider establishing a pollinator garden to attract beneficial insects and promote biodiversity. Additionally, designate a space for composting, rainwater harvesting, or seed-saving activities to incorporate sustainable practices into your gardening routine. By planning for specialty areas, you can nurture your specific gardening interests and create a garden that suits your unique needs.
Crop Rotation and Succession Planting
Understanding Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a technique in which different plant families are grown in a specific sequence to minimize pest and disease problems while optimizing soil health. It involves rotating crops within different beds or areas each growing season. By rotating crops, you can prevent the build-up of pests and diseases that may target specific plant families. Additionally, certain crops improve soil fertility by fixing nitrogen or breaking up compacted soil. By understanding crop rotation principles and planning your planting cycles carefully, you can create a more sustainable and productive garden.
Benefits of Succession Planting
Succession planting is the practice of planting crops in intervals, ensuring a continuous supply of fresh produce throughout the growing season. Instead of planting everything at once, you stagger plantings at regular intervals, allowing for a steady harvest over an extended period. This technique maximizes space utilization, avoids gluts or shortages, and extends the productivity of your garden. For example, you can sow a new crop of lettuce every two weeks rather than planting all the seeds at once. By incorporating succession planting into your garden plan, you can enjoy a continuous harvest while optimizing your planting space.
Planning for Continuous Harvest
Combining crop rotation and succession planting techniques can result in a garden with a continuous harvest. Start by dividing your planting areas into beds or sections. Rotate crops within each bed, ensuring that different plant families follow one another in a logical sequence. Within each bed, practice succession planting, sowing seeds or transplanting seedlings at regular intervals. By carefully planning and timing your plantings, you can harvest crops throughout the growing season, providing you with a steady supply of fresh produce. This approach maximizes the productivity of your garden and ensures you can enjoy garden-fresh vegetables for an extended period.
Improving Soil Health
Testing Soil Composition
Before you can effectively improve soil health, it’s essential to understand its composition. Conducting a soil test will provide you with valuable information about the pH level, nutrient content, and organic matter percentage of your soil. Depending on the results, you can adjust the soil’s pH through additions of lime or sulfur, and address nutrient deficiencies by adding organic amendments or fertilizers. By testing your soil, you can ensure it provides the optimal environment for plant growth and vitality.
Amending the Soil
Amending the soil refers to the process of adding organic matter or supplements to improve its fertility, structure, and moisture-holding capacity. Common soil amendments include compost, aged manure, leaf mold, and peat moss. These materials enrich the soil with essential nutrients, improve drainage, and promote beneficial microbial activity. Before planting, work the amendments into the top layer of soil, ensuring they are evenly distributed. Repeat this process annually to maintain soil fertility and structure. By amending your soil regularly, you can create a nutrient-rich environment that supports healthy plant growth.
Implementing Cover Crops
Cover crops, also known as green manure, are plants that are intentionally grown to improve soil health and fertility. Cover crops help prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and add organic matter to the soil when their biomass is turned under. They also help break up compacted soil, increase water infiltration, and promote beneficial soil microorganisms. Common cover crop choices include legumes such as clover or peas, which fix nitrogen in the soil, and grains like rye or oats, which add organic matter. By incorporating cover crops into your garden rotation, you can improve soil health and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Optimizing Watering Systems
Choosing the Right Irrigation Method
Efficient watering is crucial for a productive garden. The choice of irrigation method depends on factors such as the size of your garden, the water source available, and your personal preferences. Common irrigation methods include overhead sprinklers, soaker hoses, and drip irrigation systems. Overhead sprinklers provide universal coverage but can lead to evaporation and water waste. Soaker hoses deliver water directly to the plant’s base, reducing water loss, but may require frequent manual adjustment. Drip irrigation systems deliver water precisely to the plant’s root zone, reducing evaporation and ensuring efficient water usage. Select the irrigation method that best suits your garden’s needs and promotes water conservation.
Utilizing Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient watering method that delivers water directly to the plant’s root zone. This technique uses perforated hoses or tubes with emitters that slowly release water along the plant rows. Drip irrigation minimizes water waste by reducing evaporation and runoff. Additionally, it promotes deep root growth, which leads to healthier, more drought-tolerant plants. Drip irrigation systems can be set up on timers, making it easy to water your garden consistently, even when you’re away. By utilizing drip irrigation, you can optimize water usage, save time and effort, and ensure your plants receive the water they need for maximum productivity.
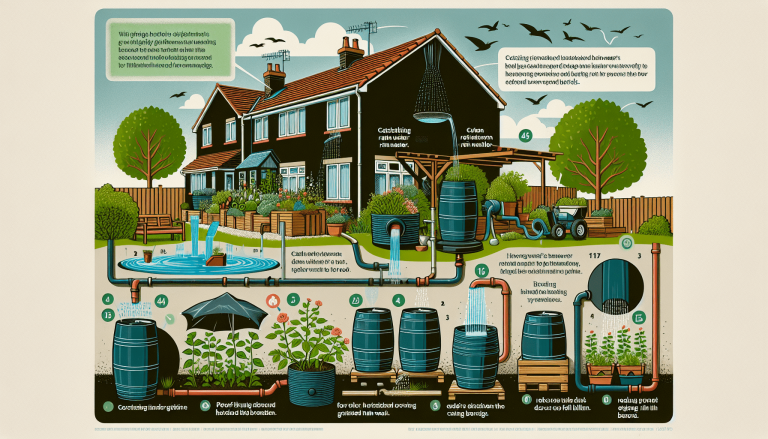
Water Conservation Techniques
Conserving water is not only environmentally responsible but also important for maintaining a productive garden. Several techniques can help you optimize water usage and reduce waste. Consider applying mulch around your plants to conserve moisture and suppress weed growth. This helps prevent evaporation and keeps the soil cool and moist. Additionally, collect rainwater in barrels or use a rainwater harvesting system to supplement your watering needs. Water your garden during the cooler hours of the day to minimize evaporation, and avoid overwatering by monitoring soil moisture levels. By incorporating water conservation techniques into your gardening practices, you can make the most of this precious resource while promoting a thriving garden.
Prioritizing Plant Diversity
Benefits of Plant Diversity
Plant diversity refers to the variety of different plant species and varieties grown in your garden. Prioritizing plant diversity offers numerous benefits for your garden’s productivity and overall health. Different plants have varying nutrient requirements, growth habits, and pest resistance. By growing a diverse range of plants, you can decrease the risk of nutrient deficiencies or imbalances and reduce pest and disease problems. Plant diversity also attracts a wider array of beneficial insects and pollinators, which help with pollination and pest control. Additionally, a diverse garden is visually appealing and can provide a continuous supply of fresh produce throughout the growing season.
Complementary Plant Pairings
Complementary plant pairings, also known as companion planting, involve strategically placing plants together to benefit one another. Certain combinations of plants can repel pests, attract beneficial insects, or enhance each other’s growth and flavor. For example, planting marigolds or nasturtiums alongside vegetables can deter pests such as aphids or nematodes. Growing aromatic herbs, such as basil or rosemary, near tomatoes can improve the tomatoes’ flavor and repel certain insect pests. By understanding the synergistic relationships between different plants, you can create a garden that thrives with minimal intervention.
Comprehensive Plant Selection
When selecting plants for your garden, consider a comprehensive range of options to maximize productivity and diversity. Choose a mix of annuals and perennials to provide continuous harvests and long-term garden structure. Select a variety of vegetables, fruits, herbs, and flowers to cater to your culinary and aesthetic preferences. Incorporate native plants or heirloom varieties to promote biodiversity and preserve genetic diversity. Consider experimenting with new or unusual plant varieties to broaden your gardening horizons. By embracing a comprehensive plant selection, you can create a garden that is both productive and beautiful.
Implementing Pest Control Measures
Identifying Common Garden Pests
Garden pests can pose significant challenges for gardeners, potentially damaging crops and reducing productivity. It is essential to identify common garden pests in your area to effectively implement pest control measures. Common pests include aphids, slugs, snails, caterpillars, and various types of beetles. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pest activity, such as chewed leaves or discolored foliage. Early detection can help you take prompt action and reduce the impact of pests on your garden. By familiarizing yourself with common garden pests, you can be proactive in preventing and managing their presence.
Natural Pest Control Methods
Preventing and managing garden pests can be achieved through a variety of natural methods that minimize the use of pesticides. Encourage beneficial insects such as ladybugs, lacewings, or parasitic wasps to establish in your garden. These insects prey on common garden pests, providing natural pest control. Planting companion plants that naturally repel pests or attract beneficial insects can also help reduce the need for pesticides. Physical barriers such as netting or row covers can protect plants from pests while allowing for airflow and sunlight. Implementing crop rotation and practicing good garden sanitation, such as removing plant debris, can also play a vital role in pest management.
Minimal Chemical Approach
While chemical pesticides can be effective in controlling garden pests, they should be used sparingly and as a last resort. Chemical pesticides can harm beneficial insects, pollinators, and the environment. If the use of pesticides becomes necessary, opt for organic or biopesticides that are less harmful to the environment and non-target organisms. Always read and follow the instructions on the pesticide label carefully, and avoid using broad-spectrum pesticides that may kill beneficial insects. By taking a minimal chemical approach, you can maintain a balanced ecosystem in your garden and protect the overall health of your plants.
Maintaining a Garden Calendar
Keeping Track of Planting Dates
Maintaining a garden calendar is an essential tool for staying organized and optimizing your garden’s productivity. Recording planting dates allows you to plan successive harvests, stagger planting intervals, and ensure optimal growing conditions for different crops. Note the recommended planting dates for each vegetable, fruit, or herb variety you intend to grow, taking into account your local frost dates and any specific climatic considerations. By keeping track of planting dates, you can stay on top of your gardening schedule and maximize your garden’s potential.
Recording Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance tasks, such as watering, fertilizing, pruning, and weeding, are crucial for a healthy and productive garden. Keeping track of maintenance tasks in a garden calendar helps ensure that nothing is overlooked or neglected. Schedule routine tasks based on the specific needs of your plants, taking into account factors such as watering frequency, nutrient requirements, and growth habits. By recording maintenance tasks and setting reminders, you can establish a consistent routine that promotes optimal plant growth and reduces the risk of problems.
Managing Harvest Periods
Harvesting at the right time is essential for ensuring peak flavor, nutritional value, and overall productivity. Different crops have different signs that indicate they are ready to be harvested, such as color changes, firmness, or size. By monitoring your plants and recording observations in your garden calendar, you can track their progress and harvest at the optimal time. Additionally, noting the yields and quality of your harvests allows you to evaluate the success of your gardening practices and make adjustments for future seasons. By managing harvest periods effectively, you can enjoy the rewards of your hard work and maximize the productivity of your garden.
In conclusion, planning a garden layout for maximum productivity involves careful consideration of various factors such as light conditions, soil quality, available space, functional zones, crop rotation, soil health, watering systems, plant diversity, pest control measures, and maintaining a garden calendar. By understanding and implementing these principles, you can create a garden that is not only visually appealing but also highly productive, providing you with an abundant supply of fresh, homegrown produce throughout the growing season. Happy gardening!